Inverse folding based pre-training
Adding to the toolbox for deep leanring of RNA structures
TermNN is a tool to identify intrinsic transcription terminators in bacterial genomes. It uses a pre-training approach to implement the thermodynamic model for RNA folding into a Deep Learning framework, through which sequence and structure motif of intrinsic terminators are introduced. This proved as beneficial for the performance of the tool.
The work was published in PLOS Comp. Biol., which was alkso reported in press. Data and code for this project are available on GitHub.
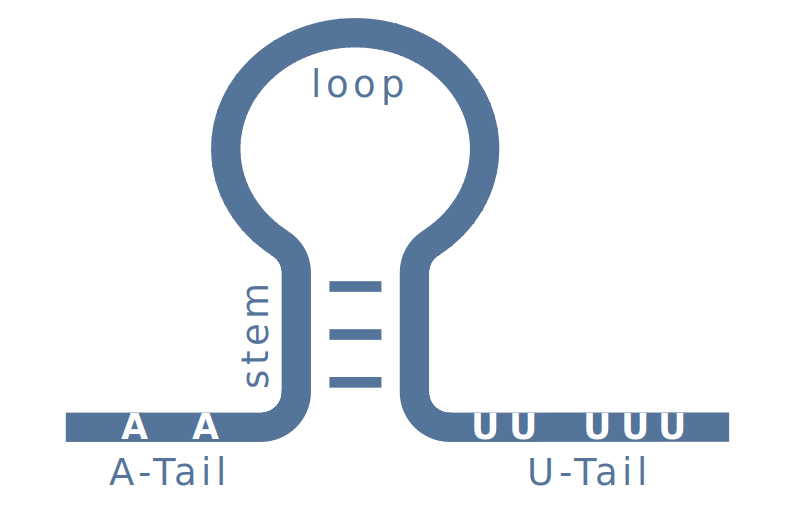

Intrinsic transcription terminators are RNA structures, which form at the 3’-end of nascent RNAs. They consist of a GC-rich stem structure, framed with an A-rich region (A-tail) and a U-rich sequence motif (U-tail). At the end of a transcribed RNA, the terminator forms a stable hairpin, which causes the RNA Polymerase to pause. At this time, the U-tail of the RNA weakly binds to the DNA, allowing the RNA to escape, which terminates the transcription.

TermNN provides Deep Learning models for the detection of intrinsic transcription terminators, based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). To enforce the learning of RNA structures, TermNN uses an inverse-folding based pre-training approach. The pre-training data feature the same structure as the terminators but have a different sequence. Additionally, two input formats are tested: The one-hot encoding reflects the RNA sequence of the input in a straight-forward maexample imagenner. The matrix encoding also reflects possible base pairings in the sequence.
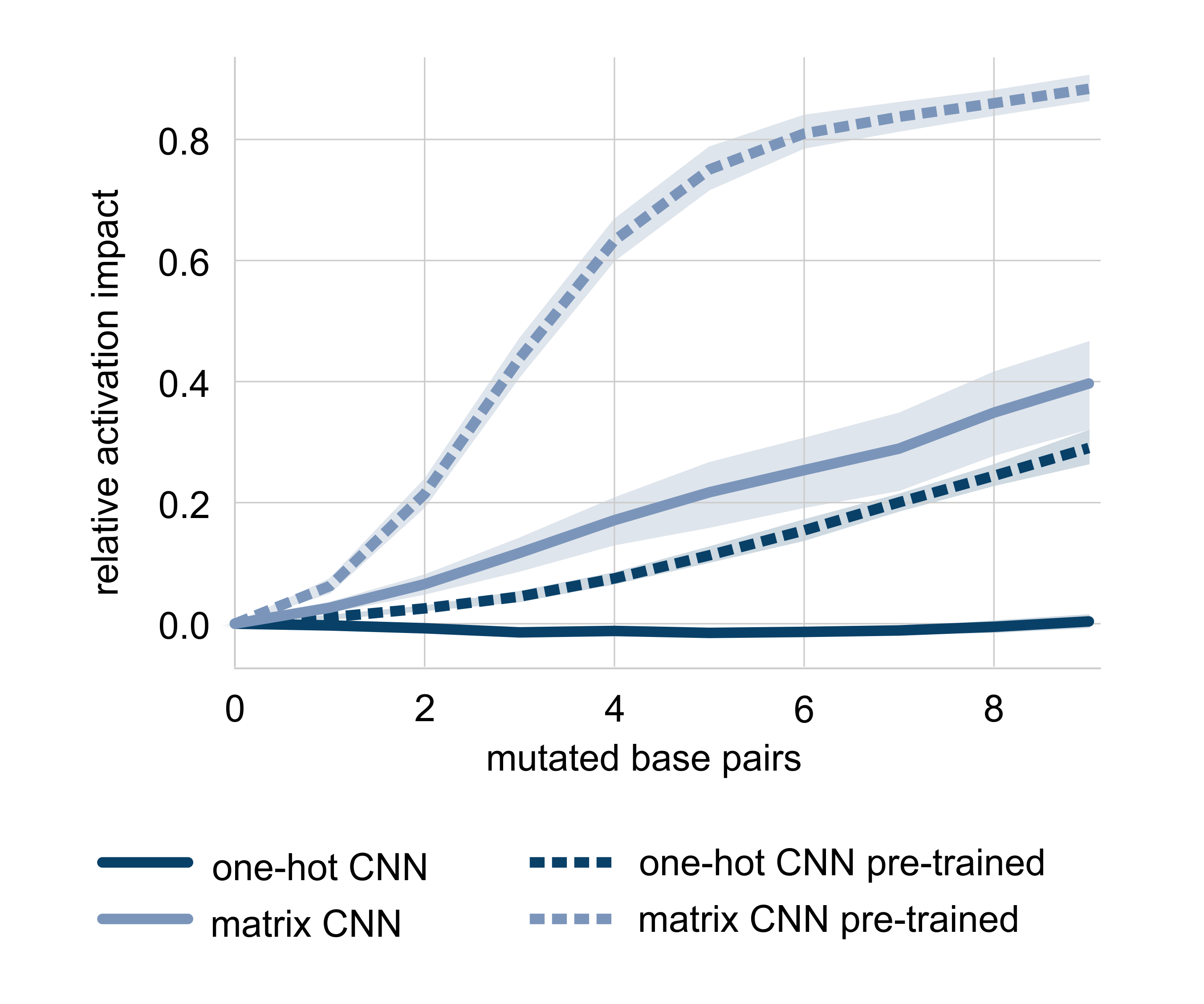

To investigate the impact of the RNA structure of transcription terminators, a growing number of mutations is inserted into the stem. Both, the input format as well as the inverse pre-training, affect the impact of the stem stability. The pre-trained matrix encoding CNN is most affected by the stem stability. In a genome-wide search for intrinsic terminators in E. coli, the pre-trained matrix encoding CNN outperformed all other models. This shows that the integration of RNA structure is beneficial for detecting terminators, and that this integration can be accomplished with the inverse-folding based pre-training approach.